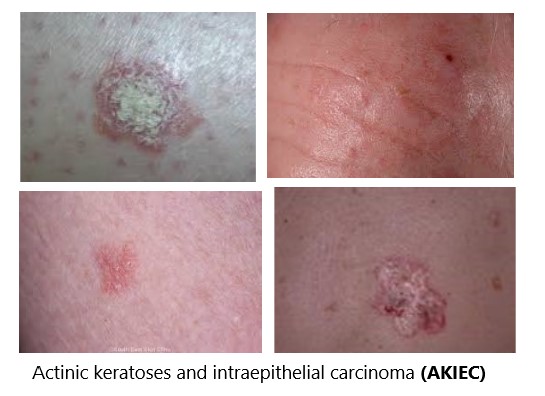
Actinic keratosis
Rough, scaly patches of skin that are considered precancerous and are due to sun exposure. Prevention is to cut sun exposure and wear sunscreen. Treatments include performing cryosurgery (freezing with liquid nitrogen), cutting the keratoses away, burning them, putting 5-fluorouracil on them, and using photodynamic therapy (injecting into the bloodstream a chemical that collects in actinic keratoses and makes them more sensitive to destruction by a specialized form of light). Also known as solar keratosis and senile keratosis
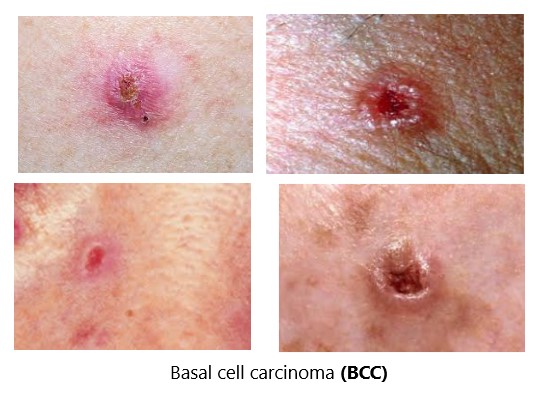
Basal cell carcinoma
is a type of skin cancer. Basal cell carcinoma begins in the basal cells — a type of cell within the skin that produces new skin cells as old ones die off. Basal cell carcinoma often appears as a slightly transparent bump on the skin, though it can take other forms. Basal cell carcinoma occurs most often on areas of the skin that are exposed to the sun, such as your head and neck. Most basal cell carcinomas are thought to be caused by long-term exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from sunlight. Avoiding the sun and using sunscreen may help protect against basal cell carcinoma.
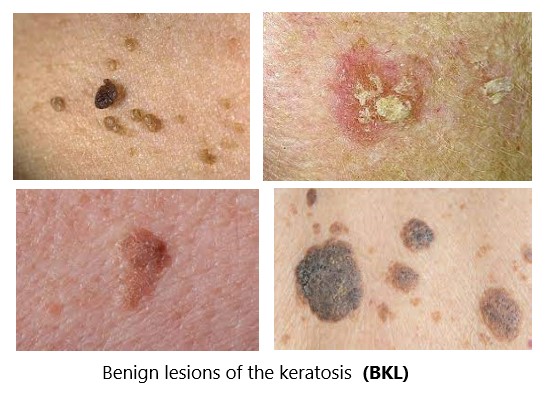
Benign Keratosis
A bkl or seborrheic keratosis is a common noncancerous (benign) skin growth. People tend to get more of them as they get older. Seborrheic keratoses are usually brown, black or light tan. The growths (lesions) look waxy or scaly and slightly raised. They appear gradually, usually on the face, neck, chest or back. Seborrheic keratoses are harmless and not contagious. They don't need treatment, but you may decide to have them removed if they become irritated by clothing or you don't like how they look.
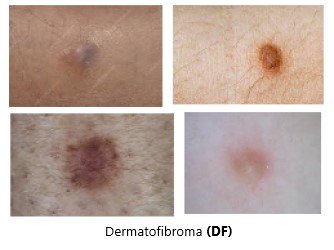
Dermatofibromas
are caused by an overgrowth of a mixture of different cell types in the dermis layer of the skin. The reasons why this overgrowth occurs aren’t known. The growths often develop after some type of small trauma to the skin, including a puncture from a splinter or bug bite n addition to minor skin injuries being a risk for dermatofibroma formation, age is a risk factor. Dermatofibromas occur more commonly in adults who are 20 to 49 years of age. These benign tumors also tend to be more common in women than men.
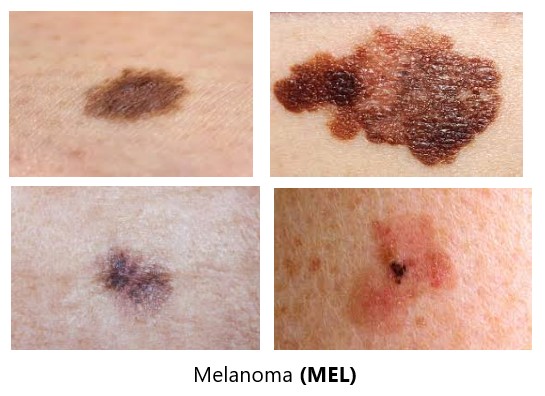
Melanoma
the most serious type of skin cancer, develops in the cells (melanocytes) that produce melanin — the pigment that gives your skin its color. Melanoma can also form in your eyes and, rarely, inside your body, such as in your nose or throat. The exact cause of all melanomas isn't clear, but exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from sunlight or tanning lamps and beds increases your risk of developing melanoma. Limiting your exposure to UV radiation can help reduce your risk of melanoma.
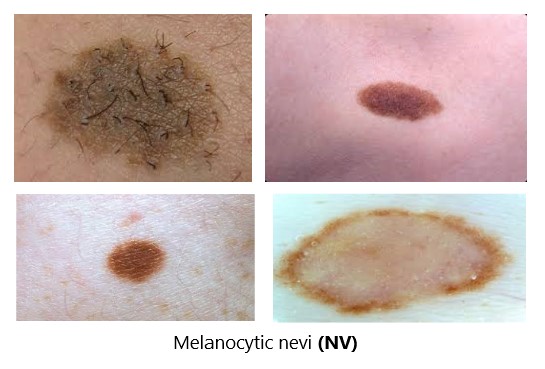
Melanocytic nevi
are benign neoplasms or hamartomas composed of melanocytes, [1] the pigment-producing cells that constitutively colonize the epidermis. Melanocytes are derived from the neural crest and migrate during embryogenesis to selected ectodermal sites (primarily the skin and the CNS), but also to the eyes and the ears. Ectopic melanocytes have been identified at autopsy in the gastrointestinal and genitourinary tracts. Congenital melanocytic nevi are thought to represent an anomaly in embryogenesis and, as such, could be considered, at least in a sense, malformations or hamartomas.
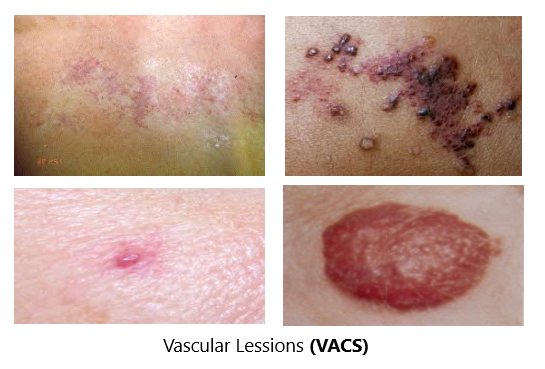
Vascular lesion
type of tumor that forms from cells that make blood vessels or lymph vessels. Vascular tumors may be benign (not cancer) or malignant (cancer) and can occur anywhere in the body. They may form on the skin, in the tissues below the skin, and/or in an organ. There are many types of vascular tumors. The most common type of vascular tumor is hemangioma, which is a benign tumor that usually occurs in infants and goes away on its own.